Reply To:
Name - Reply Comment

 Cells are the basic building block of all living beings. Cells constantly divide and replicate in order to renew, repair and contribute to the growth of an organism. Cell division is the process undergone by cells to divide and form new cells. This is a tightly regulated process that occurs throughout our lives and is vital for all living beings to exist. A variety of genes are involved in the control of cell growth and division.
Cells are the basic building block of all living beings. Cells constantly divide and replicate in order to renew, repair and contribute to the growth of an organism. Cell division is the process undergone by cells to divide and form new cells. This is a tightly regulated process that occurs throughout our lives and is vital for all living beings to exist. A variety of genes are involved in the control of cell growth and division.
Cancer results when the normal regulation of the cell cycle is disrupted. This disruption may be due to inherited or acquired genetic mutations. Thus when the cycle proceeds without control, cells can divide without an order and accumulate genetic defects that can lead to a cancerous tumor. These tumor cells may eventually spread throughout the body (metastasize) and may form new tumors.
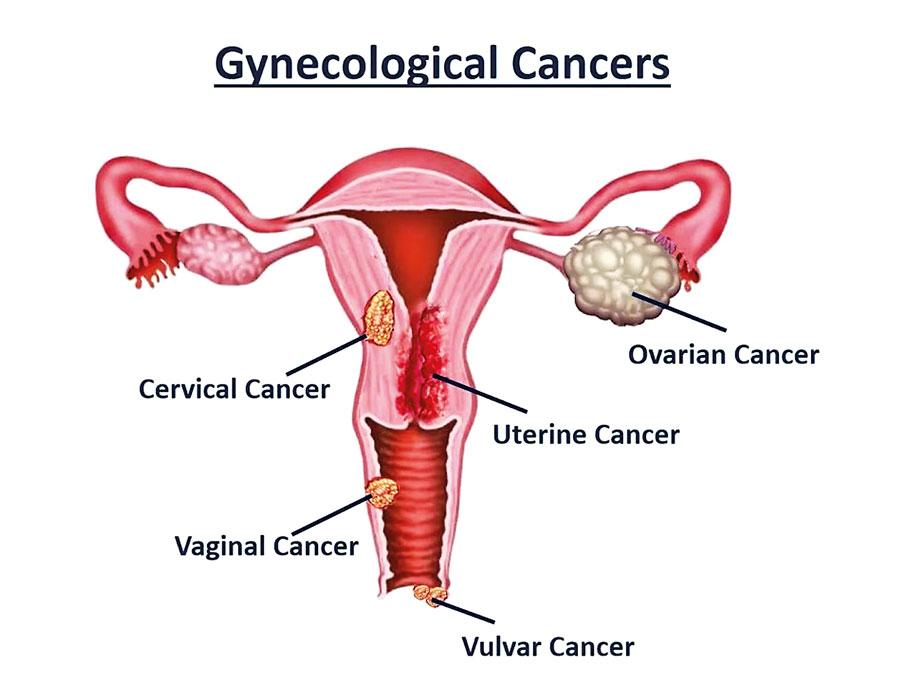
Gynecologic cancers are tumors that originate from the female reproductive organs. There are several types of gynecologic cancers which include cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal and vulvar cancers. In women related cancers, the statistics are quite standard across the world. The most common type continues to be breast cancer followed by colon, lung and gynecological cancers, especially cervical cancer.

Dr. Wong Chiung Ing, a Senior Consultant specialising in Medical Oncology at Parkway Cancer Center (PCC), specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of adult cancers, with a special interest in breast and gynecological cancers. During her recent visit to Sri Lanka, facilitated by the Parkway Patient Assistance Center (PPAC) Sri Lanka, in collaboration with Parkway Hospitals Singapore, Dr. Wong shared her insights on diagnosing, treating and preventing cancers in women.
Dr. Wong noted that the most common presenting sign of gynecological cancers is abnormal vaginal bleeding. This may present as Inter-menstrual bleeding, post menopausal bleeding, bleeding during or following sexual intercourse (post coital bleeding), or pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia). Ovarian cancer may present as abdominal distention where the patient feels full or bloated due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Gynecological organs are also proximal to the urinary bladder and rectum and some patients experience symptoms such as difficulty in urinating or defecating.
Thus, in diagnosing gynecological cancers, the first clues are the physical signs and symptoms. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound scan and histopathological techniques such as tissue biopsy are employed in arriving to a diagnosis. When the diagnosis is confirmed, usually a PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography) is done to asses if the cancer has metastasized to other organs.
Family history plays a vital role in early detection and prevention of cancer. The occurrence of ovarian cancer and breast cancer are increased in individuals who posses a gene mutation known as BRCA mutation. This mutation is inherited. In individuals with this inherited mutation, the risk of being diagnosed with (breast) cancer is up to 60%, whereas in individuals who do not possess this mutation, the risk of acquiring cancer is about 10-20%.
Individuals who have a strong family history of cancer, are advised to undergo screenings on a regular basis, as early detection is the key to successful treatment.
According to Dr. Wong, in Singapore, upon reaching 40 years of age, all women are advised to get a mammogram done every year until they are 50. If the results continue to be uneventful, upon reaching 50 years of age, a mammogram is advised to be done every 2 years until the individual is 70.
Cervical cancer can be detected at early stages with regular screening too. Dr. Wong suggests pap smear tests be done annually, in all women starting at the age of 25 years. Ideally, pap smears must be performed in all women who have had sexual contact, regardless of their age. Pap smear is best done every year, if not, at least every 3 years.
The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) test is also beneficial in assessing the probability for the development of cancer. Presence of Human Papilloma Viruses places an individual at High risk for cervical cancer, as 70-80% of all cervical cancers are caused by these viruses. Among many types of HPVs, Type 16 and 18 are associated with cervical cancer. Vaccines have been formulated for HPV and girls as young as 9 years old can receive vaccination, as this vaccine works best when administered before any possible contact with HPV. However, even vaccination cannot guarantee complete immunity from these notorious group of viruses.
Dr. Wong explained that treatment of different cancers depends on various factors, such as size of the tumor, location of the tumor, presence of metastasis and the extent of metastasis. Cervical cancer, when diagnosed in its early stages, can be treated with surgery. When detected in its advanced stages, chemotherapy along with surgery would be required. The importance of screening cannot be stressed enough as earlier the detection and diagnosis, better the treatment outcome. The treatment for ovarian cancer is usually surgery, followed by chemotherapy depending on the stage of cancer progression. Uterine cancer, is also treated with surgery, followed by chemothery or radiotherapy.
New advances and approaches in cancer treatment are ever growing. Anti- angiogenic drugs are now being employed in cancer treatment. Like all the cells of the body, cancer cells too require blood supply to derive nutrition from, for their growth. Avastin (Bevacizumab) is a type of anti angiogenic drug that aids in cutting off blood supply to the tumor, resulting in starvation of the tumor due to lack of nutrition. This is believed to slow down the growth of cancer cells, which usually shrink without adequate blood supply and thus, progression is prevented. This drug is used in combination with chemotherapy.
The use of immunotherapy has been established in some cancers such as melanoma and kidney cancer, but in breast and gynecological cancers, it is not used routinely. Immunotherapy targets certain genetic expressions on the cells, and is designed to identify the cancer cells using those tumor markers expressed, and to fight them. Dr. Wong also hopes that Immunotherapy could be employed succesfully in future. However, the advantages of Immunotherapy is still being evaluated, and its comparatively expensive, hence, it is not the standard care yet.
Well organized cervical cancer screening programmes such as regular Pap smear tests can reduce cervical cancer incidence and mortality. A pap smear test is a pain free procedure which takes under five minutes to complete. Setting aside just a day in a year for screening goes a long way in reducing the individual and global burden of cervical cancer.