
Albumin is the most abundant circulating protein found in body fluid and it represents half of the total protein content in a healthy human.
Albumin is synthesized in the liver. Within the liver cell its synthetic process is modified by many interrelated factors such as Oncotic pressure (a form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins, especially albumin in a blood vessel), malnutrition and toxins. These factors may reduce albumin production. There is a complex system for the production of proteins for export. This system consists of a strand of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to which is attached two ribosomal subunits. Larger ribosomal subunits are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. When the albumin molecule is synthesized, it is entered via the centre of the larger ribosomal and subunits into the internal space of the endoplasmic reticulum, and then, passes through both the smooth reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. It is extruded in some way directly into liver plasma.
Hyperalbumia
Abnormally high albumin levels in body fluid and Increased serum albumin level are caused by dehydration, acute infections, burns and stress from surgery or a heart attack.
Hypoalbuminemia
It is an abnormally low blood level of albumin in body fluid. The steady state concentration of albumin in plasma depends on the rates of synthesis and degradation and on its inter-compartmental distribution.
Factors associated with hypoalbuminemia
Nutrition Deficiencies (A decreased supply of amino acids and iron and zinc nutrition deficiencies affect for reduced serum albumin production)
Burns (Due to increased vascular permeability resulting in the leakage of albumin from the intravascular to the extravascular compartments)
Gut Loss (not being able to properly absorb nutrients in gastrointestinal tract by inflammatory bowel disease or lymphoma)
Chronic kidney disease (Damage of the glomerulus reasons for the increased albumin loss through urine)
Sepsis (is a life-threatening reaction to an infection such as tuberculosis)
Chronic illnesses (Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, Cardiac failure, auto immune diseases
and cirrhosis)
Complications of Hypoalbuminemia
- Buildup of fluid in legs or face
- Rough and dry skin
- Hair thinning
- Jaundice (skin that looks yellow)
- Breathing difficulties
- Fatigue
- Irregular heartbeat
- Abnormal weight gain
- Lack of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Feeling nauseous
- Vomiting
- Worsen the effects of other diseases(buildup of fluid including around the lungs and stomach)
- Pneumonia
- Muscle damage
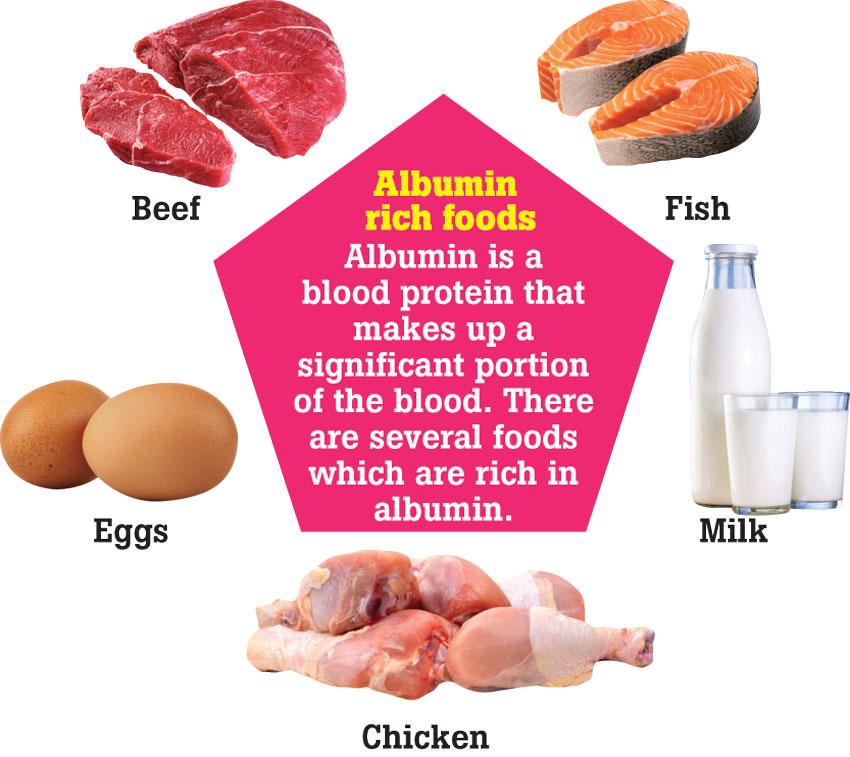
Albumin rich foods
Albumin is a blood protein that makes up a significant portion of the blood. There are several foods which are rich in albumin.
Beef
Milk
Eggs
Fish
Chicken
However person who is suffering from hypoalbuminemia, needs to obtain advice from a doctor or a dietitian in order to increase his or her plasma or serum albumin level with an albumin rich balanced diet.
The writer is a former medical laboratory technologist at a private hospital and holds a MSc. Degree in Industrial and Environmental Chemistry from the University of Kelaniya and a BSc in Food Production and a Technology Management degree from the Wayamba University of Sri Lanka.
 Albumin is the most abundant circulating protein found in body fluid and it represents half of the total protein content in a healthy human.
Albumin is the most abundant circulating protein found in body fluid and it represents half of the total protein content in a healthy human.