Cancer is not just a zodiac sign, but also considered as a disease condition which can make you struggle between life and death. Some might say that death is easier than facing a cancer because of the hardships this disease gives, making the victim suffer throughout the rest of his or her life. However, there can be hundreds and thousands of cancer survivors and people who took on life with cancer as it is, in the best way possible thanks to their strong will. Yet why I am highlighting the dark side of cancer is to make you think twice and be aware of the PREVENTIVE part-which can be practiced before this dreadful condition invades you or your loved ones.

There is a long list of different types of cancers, invading different parts of your body in a range of severities. in today’s Health Capsule we are going to shed light on Cervical Cancer-a type of cancer which conquers the cells in your cervix, multiplies and spreads to cells around too with further advancement. To know more on the etiology, risk factors, presentation and preventive measures on cervical cancer, we spoke to Dr Suranga Hettipathirana, consultant Gyaenocologist and Obstetrician, who has years of experience in diagnosing patients with cervical cancer with varying ferocities.
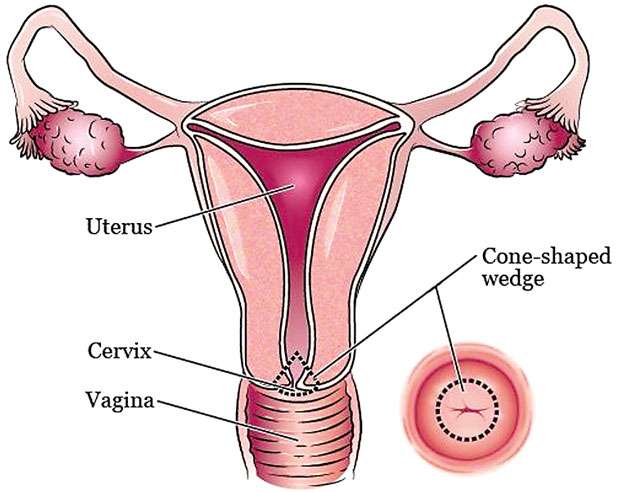
Cervix is the lowest part of your womb which connects it with the vagina. Cervical cancer occurs when cells in the cervix start multiplying in a haphazard manner thus distorting its own structure and function as well as those of surrounding structures such too, putting one’s life into danger.
“Cervical cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths globally (accounting for 80% of all deaths in developing countries). Around 1.4 million women suffer from this cancer with about 450,000 cases reported annually. In Sri Lanka the burden is more or less the same where 10% of all cancers are of the cervix. The good news is cervical cancer, when compared to other types of cancer has a slower progression so this pre-cancerous stage will provide time for early detection and prevention from further spreading. But the worst scenario is even if the preventive measures have been expanded up to a sound magnitude, Sri Lankan women still tend to forgo them, thus putting their lives at a greater risk” said Dr. Hettipathirana.
HPV the main culprit
Almost all the abnormal changes in the cervical tissue begin following the exposure to Human Papilloma Virus (99%)- rather described as a group of viruses with more than 100 different types, but few causing cancer and the rest resulting in benign warts on the skin or genitalia. More than 70% of cervical cancer cases can be attributed to two types of the virus, HPV-16 and HPV-18, often referred to as high-risk (Human Papilloma Virus) HPV types. Majority of the women who have got infected by HPV virus do not necessarily develop cervical cancer because the HPV infection in most women does not last long and tends to resolve spontaneously within 2 years. However, a minority of women with non-resolving HPV infection is considered to be at a greater risk of developing cervical cell abnormalities and malignancy. Other risk factors for cervical cancer include,
- Early attainment of puberty (early menarche)
- Late menopause
- Multiple sexual partners
- Tobacco smoking
- HIV infection
- Suppression of the immune system
- Past or current Chlamydia infection
- Overweight and obesity
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives (The risk returns to normal when the contraceptive pills are discontinued)
- Having three or more full-term pregnancies
- Family history of cervical cancer
- Low socio-economic status
“However in Sri Lanka, cervical carcinoma is known to be spreading quite vigorously among commercial sex workers so it’s always advised to have a faithful sexual partner, use barrier methods in having sexual intercourse and most of all, get yourself screened for cancer cells and vaccinated against Human Papilloma Virus” adds Dr. Hettipathirana.
Early stages of cervical cancer
Usually there won’t be any signs or symptoms at the early pre-cancerous stages of cervical cancer. Therefore regular check-ups and follow-up will support you in making an early diagnosis, providing adequate time for proper control or cure. The prognosis (chance of recovery) is better when the cancer is diagnosed early.
Most obvious complaints one would encounter as the cancer advances would include,
- Vaginal bleeding
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Significant weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Generalized fatigue, malaise and lethargy
If one or more of these signs and symptoms tend to bother you, it is highly advised to seek immediate medical advice because early diagnosis is crucial when it comes to cancerous growths.
Early diagnosis is crucial
The diagnosis of cervical cancer is made following a complete history on all your personal details related to the disease (health habits, sexual partners, socio-economic status etc.) along with a thorough physical examination followed by various investigations.
Pap Smear
This is a screening procedure for cervical cancer which is helpful in checking the presence of pre-cancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix. During the test, cells from your cervix are gently scraped out and checked under microscopy to identify abnormal cells. Pap Smear can also detect cells which can potentially give rise to cancer cells in the future which is of a great advantage to halt the development of cancer at the earliest possible stage.
Unfortunately, even if the government has provided facilities to get Pap Smears done FREE of charge, only a 5% of women population tend to make use of it, thus contributing to the rise incidence of Cervical carcinoma among the Sri Lankan women population despite the preventive care provided.
“Many women are scared to get the PAP test done as a result of the undue fear of pain, but just think TWICE whether the value of your life isn’t worth the tiny little pain you would endure in doing a test which would SAVE you from death”
Dr. Hettipathirana also highlighted the importance of getting a HPV VACCINE which has a huge protective effect against cervical cancer. This vaccine has now been added to the national immunization schedule for girls of 11-13 years of age and is also available in the private sector at a cost which ranges between Rs 10,000-15,000.
“The treatment options available for Cervical cancer depends on the extent of spread. Ones which are limited to a smaller part of the cervix can be incised even without anaesthesia and preserves your future fertility wishes, but quite extensively invaded areas will have to be treated with the complete removal of your womb, cervix, vagina as well as tubes or ovaries. This is more or less beyond the control of you or any health care professional, so I stress again to get yourself SCREENED for cervical cancer and VACCINATED against HPV because once you get caught-the escape will not be easy at all” he said.
Take home message
-Every sexually active woman should get a Pap Smear done at least once in every 3-5 years.
-No woman will die because of Cervical cancer, if they get the HPV Vaccine and pap smear done as advised.

 Cancer is not just a zodiac sign, but also considered as a disease condition which can make you struggle between life and death. Some might say that death is easier than facing a cancer because of the hardships this disease gives, making the victim suffer throughout the rest of his or her life. However, there can be hundreds and thousands of cancer survivors and people who took on life with cancer as it is, in the best way possible thanks to their strong will. Yet why I am highlighting the dark side of cancer is to make you think twice and be aware of the PREVENTIVE part-which can be practiced before this dreadful condition invades you or your loved ones.
Cancer is not just a zodiac sign, but also considered as a disease condition which can make you struggle between life and death. Some might say that death is easier than facing a cancer because of the hardships this disease gives, making the victim suffer throughout the rest of his or her life. However, there can be hundreds and thousands of cancer survivors and people who took on life with cancer as it is, in the best way possible thanks to their strong will. Yet why I am highlighting the dark side of cancer is to make you think twice and be aware of the PREVENTIVE part-which can be practiced before this dreadful condition invades you or your loved ones.