Reply To:
Name - Reply Comment
Cancer is a disease condition in which the cells of the body grow in an uncontrolled manner and becomes abnormal. When this growth is seen in the cervix, then it is calledas cervical cancer. Cervix is the neck of the womb/uterus or the narrow lower part of the womb.
What causes cervical cancer?
There are many risk factors for cervical cancer. The main cause of this cancer is a virus called the Human Pappiloma Virus (HPV). HPV almost always is the cause. There are many types of HPV viruses. Not all types cause the cancer. Specifically 2 types causes 70% or more of cervical cancer. This virus is transmitted from person to person by sexual intercourse; hence it’s a sexually transmitted virus.
In most, the virus just goes away or the body gets rid of it without any consequences or harm. But in a few it goes on to cause cancer in the cervix. Once the virus invades the cells, it could take up to 8-10 yrs for the cancer changes to occur. Some types are more dangerous than the others.
Who is at risk for cervical cancer?
HPV infection:
Cervical cancer is the most common cancer in women age under the age of 45yrs. The women, who become sexually active from youngage or having multiple partners, are at high risk contracting the virus. Unprotected intercourse increases the risk of contracting the virus.99% of cases, cervical cancers are caused by persistent infections whiletransmitted through skin to skin contacts in the genital area
Sexually transmitted disease:
Presence of other sexually transmitted diseases like Chlamydia etc further increases the risk.
Weakened immunity:
HIV and AIDS add more risk since it compresses the immunity. Also people, who are on immune suppressive drugs such as e.g. after transplant, also have a higher risk.
Smoking:
Women who smoke are found to have higher incidence of cervical cancer. Lining of the cervical cells are damaged by chemicals found in the smokehence increasing the chance of the virus invading the cells and changing them into cancerous cells.
Pregnancy and child bearing:
There is some evidence to suggest that women who have children too early or having too many, are also linked with high risk factors. Especially women bearing kids before the age of 17years are at more risk than woman who has her first child after 25years. Also having more than 7 children have shown to increase the risk of developing cervical cancer than women who have never given birth.
Birth control/Contraceptive pill:
Use of certain pills for longer term (I.e. over 5 years) may increase in the chance of having cancerous cells. However, in contrast use of pills is known to be protective against ovarian and womb cancer.
Family:
There may be evidence to suggest that this cancer may also run in some families.
Other risks:
Women from a deprived background are found to be more at risk.
Women who were exposed to a drug that was used in 1940’s called Diethylstilboestrol (DES) are at high risk as well. Certain other chemical exposures are also linked with cervical cancers as well.
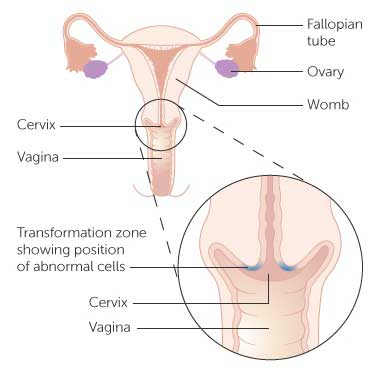
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
Early stage of this cancer can be almost symptomless. Hence the cervical screening i.e.PAP test is a lifesaving screening tool and it is a must for women who are sexually active.
Abnormal/unusual vaginal bleeding which can occur after sexual intercourse, in between periods or after the menopause is noted as a major symptom. Some women have unpleasant vaginal discharge or some discomfort with sexual intercourse. As one can appreciate that all those above mentioned symptoms are very non specific and there could be many other reasons for all the symptoms as well. So the importance of regular cervical screening is the utmost way of early detection.
How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
High level of suspicion is vital to diagnose this condition in our country since routine recall is not practiced well. Cervical smear or a PAP test is an effective tool used for the diagnosis of pre cancerous cells or even cancerous cells. Also cervical biopsies or colposcopies (a large microscopy that visualizes the cervix) are also used in the diagnosis. Even though it takes long time i.e. up to 10years or more for the cancer changes to occur in these cervical cells, they can still be detected at the precancerous stage if cervical smears are done routinely. In one study it was noted that up to 850-950 women are admitted every year to government hospitals in our country with advanced disease due to the lack of screening.
How is cervical cancer treated?
First of all once the precancerous cells are identified, they are removed or destroyed from the body to prevent them from further changing into cancer cells. They are simply shaved off from the top of the cervix or womb is removed. These cells are destroyed using Cryotherapy (freezing) or destroyed with laser or current.
Treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage of the cancer. The size and the depth of invasion dictate the treatment methods. In early stages it could be effectively dealt with surgery.Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment optionsdiffer: surgery, chemotherapy (drugs given to destroy the cancer cells), radiotherapy or combinations. If it’s incurable palliative therapy is given to relieve symptoms and make the patient comfortable.
Who should get Pap tests and how often?
Different countries have different age for starting the screening. Most have a routine recall as well. But in our country it is not so common practice thought it is important as discussed earlier.
In most countries screening begins at the age of 25years, since cervical cancer is rarely seen below the age of 25years. Ideally once a woman becomes sexually active smear test becomes an essential. Recommendations are to carry on screening every three years till the age of 49. From the age of 50 to 64 five yearly screening is recommended. After 65 it’s only needed if screening was never performed or the woman had an abnormal smear in the recent past.
What is the chance of recovery from cervical cancer?
This again solely depends on the stage of the disease. Very early detection of the disease with timely treatment may result in 95% survivingfor 5yrs or more. In advanced stage the survival rate drops drastically down to 5%.
What can a woman do to decrease her risk of getting cervical cancer?
Dr. (Mrs) Roshan Zeirideen Zaid
MBBS (CEY) MRCOG (UK), CCT (UK), DFSRH (UK),
Fellowship in Gynae Laparoscopy (India)
Resident Consultant Obstetrician
Gynecologist, Laparoscopic Surgeon & Fertility Specialist
Nawaloka Hospitals