Reply To:
Name - Reply Comment
According to the WHO, about 210 million pregnancies occur each year worldwide, of which 87 million are unplanned, of which 41 million continue to birth
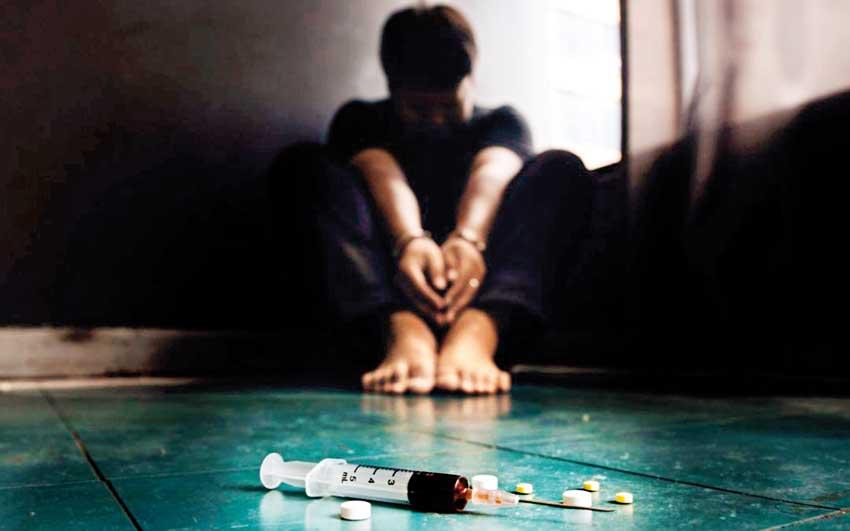
The number of the youth population aged between 15 to 25 entering treatment for drug-related problems has risen by 166% from 2010 to 2018
 The use of illicit or illegal drugs or alcohol is known as substance use and the use of medicinal drugs for purposes other than those for which they are meant to be used, or in excessive amounts is defined as substance abuse.
The use of illicit or illegal drugs or alcohol is known as substance use and the use of medicinal drugs for purposes other than those for which they are meant to be used, or in excessive amounts is defined as substance abuse.
Drug addiction and substance abuse have become a major public health and a social problem around the world. Mostly the offenders and victims of drug users being adolescents.
Sexual harassment, previous experience with drugs, and peer pressure are some of the external factors which push them to drug addictions. This gets further complicated when the addict contracts HIV/AIDS, unplanned pregnancy, and suffers from mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Commonly, drugs are categorised into two types such as licit drugs and illicit drugs.
Alcohol, tobacco, could be considered as examples of licit drugs on the market.
Illicit drugs are obviously prohibited by law and hence illegal to make, sell or use.
Illicit drugs have been classified as illegal drugs because they are a threat to the health and life of the victims and society at large. Heroin, cocaine, LSD, ecstasy, Methamphetamine, Amphetamines, and other hallucinogens are some examples of these types of drugs. These are highly addictive and pose serious risks to those who use them.
Opium and Cannabis are two illegal drugs that are prevalent in Sri Lanka. However, Opium and Cannabis have also been used in traditional ayurvedic medical preparations.
The 1980s was a turning point in Sri Lanka with changes in socio-economic policies and the north and east ethnic violence which helped increase drug smuggling.
Especially when children are forced to learn online and most of the time they had to sit in front of the screen, without peer to peer interaction.
This has been exacerbated during the global pandemic of Covid-19 due to the lockdowns and school closures and many suffered from anxiety and depression.
Especially when children are forced to learn online and most of the time they had to sit in front of the screen, without peer to peer interaction.
Not only that, many of the children were at risk of exposure to online sexual predators, online gaming, and criminal social media networks.
A child can become an addict by genetic composure or by environmental factors
The diverse effects and consequences of drug addiction are vast and varied and affect people of all ages.
Researchers have found how depression, anxiety, memory loss, aggression, mood swings, paranoia, and psychosis are found to be connected to emotional well-being.
A sense of hopelessness, loneliness, fear, guilt, shame, and unhappiness are negative emotions felt by drug addicts.
This in turn affects their family members. It may tend to disrupt family relationships because drug abuse leads to domestic violence and related problems.
Reports say in Sri Lanka the number of youths between 15 and 25 entering for treatment for drug-related problems has risen by 166 % from 2010 to 2018.
Meanwhile, intravenous drugs use is one of the causes of HIV/AIDS transmission. Sharing syringes facilitate its spread.
Unintended pregnancies are another troubling public health issue among teenagers and adolescents.
According to the World Health Organisation, approximately 210 million pregnancies occur each year worldwide of which 87 million are unplanned and 41 million continue to birth.
According to reports the total number of unsafe abortions in 2008 was 21-22 million worldwide and there were 22 unsafe abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years.
Most of the younger generation are exposed to substance use because of family issues such as divorce or separation of parents, neglect from their own family, family breakup, and broken love affairs.
A range of school problems like failure in grading, poor performance, placement in a special class, early dropping out, and a lack of commitment to education have been viewed as common antecedents to the initiation, use, and abuse of drugs.
Association with drug-using peers is perhaps the strongest supported predictor of adolescent substance use.
Teenagers may use drugs as a means of temporarily alleviating discomfort connected to life events which they perceive as being out of their control and can be seen as contributing significantly to an understanding of the higher incidence of drug use among teenagers and those from disrupted families.
Teenage pregnancy becomes a social issue when teenagers who are in poor academic achievements sometimes become sexually active and early parenthood in schools.
Girls under 16 are five times more likely to die during or immediately after pregnancy than women 20 to 24. Their infants have a higher incidence of toxaemia, anaemia, nutritional deficiencies, low birth weight, and retardation than infants of older women.
Due to those social impacts, most of them, unfortunately, chose to harm themselves or end up in centres or other health care hospitals.
Peer pressure, self-esteem, friendship, love affairs can also affect mental health.
When teenagers are struggling with problems, they quickly turn to alcohol or drugs to escape the situation.
But in the longer term, it exacerbates them and often ends in abuse or dependence. The effects of substance use vary from adults to adolescents.
While adults tend to get more subdued and slowed down by alcohol, in adolescents it is the opposite.
Tips for parents from experts: