Reply To:
Name - Reply Comment

This article is written based on information collated through consultations that were submitted as a technical report recently to Gotabaya Rajapaksa and other relevant government authorities. The consultations were among those who had been interested in dam safety and directly involved in managing the “Narrowly-Missed” breach and in the reconstruction of the Parakrama Samudraya bund after the Cyclone in 1978. They considered it appropriate in sharing concerns and acquired knowledge with the public at this crucial juncture of decision-making on the safety of the aging irrigation infrastructures in Sri Lanka.
recently to Gotabaya Rajapaksa and other relevant government authorities. The consultations were among those who had been interested in dam safety and directly involved in managing the “Narrowly-Missed” breach and in the reconstruction of the Parakrama Samudraya bund after the Cyclone in 1978. They considered it appropriate in sharing concerns and acquired knowledge with the public at this crucial juncture of decision-making on the safety of the aging irrigation infrastructures in Sri Lanka.
The Parakrama Samudra Reservoir was built by King Parakrama Bahu during his reign (1153-1186 AD) and it has a reservoir capacity of 116,000 acre-feet, feeding approximately 25,000 acres of paddy cultivation. This reservoir has a bund 52 feet high and 10 miles long.
The study on Parakrama Samudra bund was undertaken owing to information and misinformation that had been widely shared and debated in the formal media, and especially in the social media, concerning Parakrama Samudra bund being proposed as a site to construct an 8-feet wide walking path. Further, it is noted that similar walking paths will be constructed on bunds of other reservoirs such as Kanthale, Udukirala Wewa, etc.
"It appears that ad hoc decisions have been taken for reasons unknown. The lack of laws and dam safety regulations in Sri Lanka could be one of the reasons for such ad hoc decisions taken by various individuals and organisations"
Cyclone in 1978
The 1978 Cyclone started with the onset of the storm formed on November 20, 1978 over the southwest Bay of Bengal. It intensified gradually, reaching Super Cyclonic Storm Status Category 4 Cyclone on November 23 with a gusty wind speed of 220 km/h. The 1978 Cyclone was the second strongest Super Cyclonic Storm to strike Sri Lanka’s Eastern Province since modern records began. The cyclone attained peak intensity on November 23, before making landfall in Batticaloa. The Eastern Province was heavily affected by the cyclone.
The cyclone had devastating impacts in Sri Lanka, killing about 915 people and an unaccounted number of cattle and other animals. An estimated more than one million people were affected, with over 250,000 buildings damaged, and one-fifth of Batticaloa’s fishing fleet destroyed. Nine of the eleven paddy stores were destroyed and 90% of the coconut plantation (about 28,000 acres) in the Batticaloa district were destroyed. Also, in Polonnaruwa District, the public and private infrastructure, paddy, and rice stored in Food Commissioners and Cooperatives, coconut cultivation, etc., were devastated.
Cyclone 1978 and Parakrama Samudra
The Cyclone reached the Parakrama Samudra bund at about 6:30 pm on November 23 and lasted till about 4:00 am on November 24. According to eyewitnesses, the height of the waves was 10 to 12 feet. Knowing the imminent catastrophic danger of overtopping leading to a breach of the bund, the Irrigation Engineer in charge of Polonnaruwa A. D. S. Gunawardana, the Government Agent Polonnaruwa Austin Fernando, and a few other officials on duty decided to be ready with a few bulldozers and retain them standby at strategic locations such as at the sluice and spillway, to breach the bund at these locations if the need arises.
The idea behind this decision was if the predicted overnight rainfall occurred and the anticipated inflow to Parakrama Samudra did really eventuate, the inflow would have been greater than the outflow with all 10 radial gates and the sluice gates kept open. Then there was a risk of overtopping and breaching the bund. Hence, an artificially introduced breach of the bund to discharge floods along the existing channels would prevent a haphazard catastrophic breach at an unknown and unwanted location, which could inundate the heavily populated downstream areas. Such an emergency rapid drawdown is the standard practice to prevent a dam breach. Fortunately, predicted overnight rainfall was low. However, the drawdown of the reservoir continued overnight.
Following the overnight drawdown, about 2/3 of the 12-feet wide bund top road and a fair portion of the upstream shoulder were found to be slipped into the reservoir, leaving only about 1/3 of the bund top road intact. There were widespread such slips along the full length of the bund. The damaged areas were repaired with earth-fill and Ralapanawa reinstated as a short-term risk reduction measure. The upstream face of the Ralapanawa was not flattened to improve the safety margin (i.e., Factor of Safety) of the bund in case of future similar drawdowns as it was a long-term risk reduction measure to be implemented by the Government Authorities. Therefore, consideration should be given to implementing appropriate long-term risk reduction measures.
"Several long tension cracks, sealed with tar, are present on the bitumen surfaced bund top road as seen in videos of Sri Lanka media. Most of them are located along (parallel) the bund top road, thus increasing the risk of sliding failures similar to those that occurred during "
Walking Track Proposal
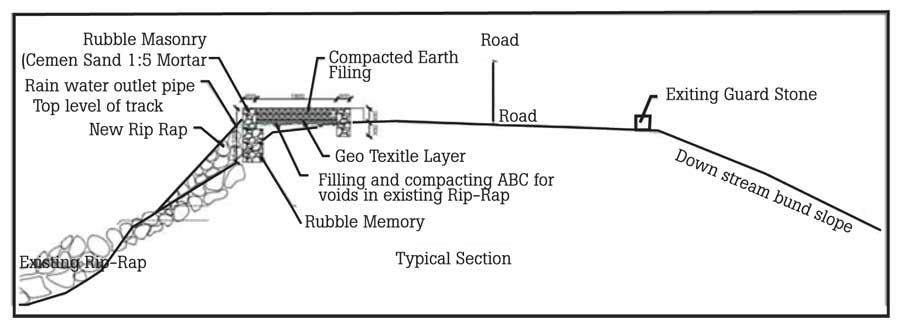
Based on information available to date, the proposed walking path will be constructed on the upstream side of the bitumen surfaced bund top road where there was a sliding failure during the 1978 cyclone and floods (See Figure 1).
Figure 1 – Typical section of the crest of the dam or bund showing the proposed walking path found in the social media, presented during the Webinar organized by the Institute of Engineers (Sri Lanka) and shown on Sri Lanka TV.
Several long tension cracks, sealed with tar, are present on the bitumen surfaced bund top road as seen in videos of Sri Lanka media. Most of them are located along (parallel) the bund top road, thus increasing the risk of sliding failures similar to those that occurred during the 1978 floods. Additional loads due to the construction of a walking path would widen and deepen those tension cracks, compromising the safety of the bund, which is not known.
Therefore, it is the considered view that additional loading on top of the 1978 sliding mass for construction of the walking path would increase the risk of reactivating the 1978 slides during a future rapid drawdown, similar to in 1978.
It is understood and appreciated that the Irrigation Department is currently undertaking geotechnical investigations to assess the safety margin of the bund.
"the 1978 floods It is to be stressed that this stretch of land along the bund is a critical area to ensure the safety of the bund. Identification of dam safety features such as heaving the ground, cracks, wet areas, springs, seepage locations, etc., in this area, is critical"
The highest concern is dam-safety
Based on information available, it is understood that there is a period of 741-years (i.e., from 1159 to 1900), where the performance of the bund is not documented and unknown. However, it is reported that the bund was totally breached during the colonial era. According to R. L. Brohier, the bund and the reservoir were abandoned for more than a century.
Given that the population at risk in case of a dam break is extremely high, it appears that the consequence category of this bund is “Extreme” as per the current international dam safety guidelines. Therefore, the proposed walking path at Parakrama Samudra cannot be compared to that of the Kurunegala Wewa, Boralesgamuwa Lake, etc., constructed along the reservoir rim, and the walking paths constructed around water bodies in the suburbs of Colombo.
It is understood that the Parakrama Samudra is formed by combining three reservoirs of unknown history. Therefore, the bund may have been raised in several stages during the 741-years associated with unknown performance.
It is not known whether dam safety-related defects of the bund such as slips or slides, cracks, animal burrows, sinkholes, soft areas, root bowls, zones of desiccation cracking, zones of residual shear strength because of historical failures, etc., were repaired to satisfactory standards, or not.
The aging of dams constructed of earth and rockfill material is due to time-related changes in the properties of the materials of the structure and its foundation. As reported in a technical paper published in May 2010 by the United States Society of Dams, the aging or deterioration of embankment dams and their foundations are of concern. These concerns extend throughout the entire life of the dam until safe abandonment or demolition.
Recent interventions on dam-safety
Given the dam safety issues associated with this controversial walking path project, the Water Forum of the Institute of Engineers in Sri Lanka conducted a Webinar on September 9, 2021 on “Usage of Inland Water Bodies for Recreation”. More than 280 personnel, mainly engineers, participated in this Webinar and raised over 100 questions related to the safety of the bund. Several questions were raised on fundamental errors and potential failure modes associated with the proposed walking path. It appears that ad hoc decisions have been taken for reasons unknown. The lack of laws and dam safety regulations in Sri Lanka could be one of the reasons for such ad hoc decisions taken by various individuals and organizations.
"Given that the population at risk in case of a dam break is extremely high, it appears that the consequence category of this bund is “Extreme” as per the current international dam safety guidelines. Therefore, the proposed walking path at Parakrama Samudra cannot be compared to that of the Kurunegala Wewa, Boralesgamuwa Lake, etc."
As far as dam safety regulations are concerned, India is well ahead of Sri Lanka. Even Ghana in Africa has introduced Dam Safety Regulations to ensure the safe design, construction, operation, and maintenance as well as decommissioning of dams.
Based on statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents, 48% of dam failures are related to overtopping and failures of appurtenant structures, and 46.5% are due to internal erosion. Due to the absence of an internal filter system in this bund, not only the slope instability, but the internal erosion is also likely to be a prominent potential failure mode.
It is understood that planning is underway to construct several fast-food outlets, toilet facilities (including a “changing room”) at the toe of the bund, i.e., within the reservation area of the bund located immediately downstream of it. It is to be stressed that this stretch of land along the bund is a critical area to ensure the safety of the bund. Identification of dam safety features such as heaving the ground, cracks, wet areas, springs, seepage locations, etc., in this area, is critical. Digging of lavatory pits, trenches, etc., could intercept permeable layers in the foundation and may trigger “backward erosion tunnels” leading to piping, which is a major failure mode in embankment dams (or, bunds). Excavations in this area could lead to sides of the downstream face of the bund, compromising its safety margin.
Should there be a need to improve the safety margin of the bund, additional stabilizing fills are to be constructed in this area over the downstream face of the existing bund. An access road along the downstream toe of the bund is an essential item for repairs and routine maintenance of the bund. Given the proximity to the dam, this reservation area should be used to stockpile materials to be used during dam emergencies such as filter sand, crushed rock, rockfill, etc., and movement of construction machinery for maintenance and repairs. This area is an integral part of the bund, hence should not be used for either permanent or temporary constructions. Therefore, consideration should be given to providing these facilities at an alternate suitable location, perhaps close to the Government Agent’s residence, or thereabouts.
Recommendations to maintain Dam safety
Based on dam safety concerns and consequences discussed, it is recommended that,
(The author can be contacted on email: [email protected])
