Reply To:
Name - Reply Comment

Sri Lanka's economic crisis forced consumers to queue up for days to buy a LP gas cylinder
Despite the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020-2021, Sri Lankan economy has been hit by the economic crisis in 2022. The article discusses the genesis and ramifications of the economic crisis in the short and long terms.
hit by the economic crisis in 2022. The article discusses the genesis and ramifications of the economic crisis in the short and long terms.
Prevailing Situation of the Economic Crisis
The US dollar shortage, caused by current account imbalance and loss of access to international financial markets due to fiscal sustainability concerns, has been disrupting most of the economic activities due to a lack of imported materials, including oil, and regular power cuts. The sharp domestic currency depreciation, rise in the price level, and a tighter monetary environment exacerbated the overall business condition challenging the competitiveness.
Exchange Rate
To identify the recession of the economy, the exchange rate is one of the key determinants; The graph shows the fluctuation of the daily exchange rate from January 2020 to January 2023. A sudden increase in the exchange rate can be clearly identified after March 2022.
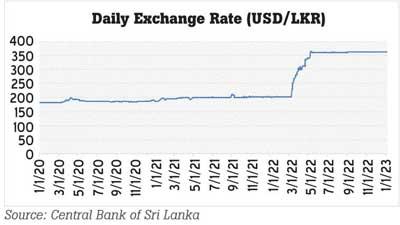
Source: Central Bank of Sri Lanka
No doubt that the economic crisis increases the price level of goods and services. Therefore, inflation targeting is also a main concern for identifying the determinants of the economic downturn.
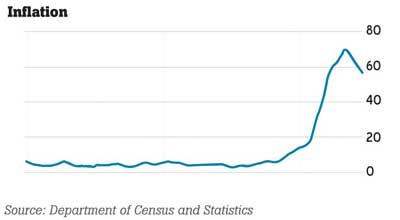
Source: Department of Census and Statistics
Economic growth has been dramatically affected by the crisis with the negative growth rate. The following graphs show that, after January 2020, the economic growth is negative. From August to October 2022, the growth rate of the economy is -11.8.
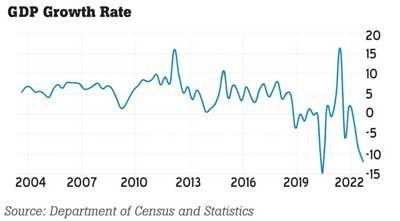
Source: Department of Census and Statistics
Causes of the economic crisis
The author believes the genesis of economic crisis occurs mainly due to the following reasons.
A lot of loans received from China and other countries has used for “politically driven popular decisions” instead of creating a productive return. The constructions of roads, playgrounds, and many other places were interesting among the political parties rather than the return on investment of the loans.
The coordination failure among the different authorities is a key factor for economic mismanagement. The coordination failure in food insecurity and high inflation created economic uncertainty that further worsened.
Popular decisions were taken for economic growth and development without proper infrastructure planning. After the war situation in Sri Lanka in 2009, everyone wishes to prop up the economic prosperity of the country. As a fact, no doubt that infrastructure development is also one of the major needs for the successful implementation of economic activities for growth. The vision of the government in this era was to suddenly expand and rehabilitate the roads, harbours, and airports. Anyway, these politically driven and improper planned decisions have directly affected the economy.
Corruption caused unbearable debt in the economy which cannot ignore as it causes the economic downturn. Therefore, numerous examples of countries with high corruption have gained negative economic growth and vice versa.
Fertilizer banned amid COVID-19 pandemic. It is common sense to policymakers to think a bit about the calamity after the pandemic. Therefore, it is not a wise decision to further exacerbate the food insecurity in the country.
The Central Bank of Sri Lanka has printed money in bulk believing that the economy to thrive according to the Modern Monetary Theory (MMT). But the printing of excessive money caused hyperinflation in the country without a proper understanding of the economic background.
Economic Theories Behind the Recession
Understanding the Business Cycle of the economy is essential for resolving the crisis. Even though the economy was under the average real GDP, the crisis can cause a deep recession over years.
Not only understanding the economic cycle is vital but also how fiscal stimulus of the economy needs to be deliberated. The following graph shows the real GDP changes with and without stimulus packages for overcoming the recession.
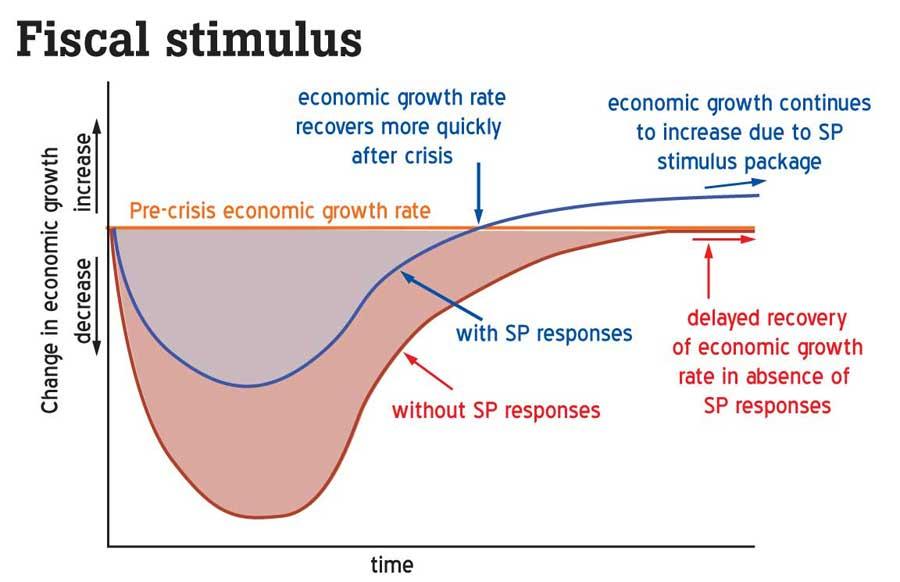
According to the above figure, economic growth can be adjusted with the stimulus package responses in the economy. As in the graph, the economic growth rate recovers more quickly after the crisis, and the growth continues to increase due to the stimulus package. Usually, the country’s macroeconomy is managed with three types of policy instruments including expenditure changing or demand policies – which alter aggregate demand for both domestic and international goods and services. Two other tools are expenditure-switching policies that modify the direction of demand between domestic output and imports such as currency depreciation and direct controls are the government restrictions on the economy such as quotas and tariffs.
Ramifications for the economic crisis
This article proposes short- and long-term ramifications for the economic crisis. Among various policy priorities, discussion with IMF and debt restructuring is the top priority. Thereby, economic and political stability can be prioritized. Furthermore, a line of credit for SMEs especially for agricultural exports and tourism can be promoted. Thus, export agriculture can earn dollars directly by promoting the exportation of agricultural products has a demanding interest among several countries. In the medium and long term the following ramifications to resolve the economic crisis can be applied.
The fiscal policy intends to use government spending, taxation, and borrowing to affect the level and growth of aggregate demand, output, and jobs. The macroeconomic situation can be changed by changing the direct and indirect taxation, like direct taxation through levied on income, wealth and profit, income tax, inheritance tax, national insurance contributions, capital gains tax, and corporation tax. Indirect taxes are taxes on spending such as excise duties on fuel, cigarettes, and alcohol, and Value Added Tax (VAT) on many different goods and services.
Monetary policy is also one of the expenditure-changing or demand-side management policies, which refers to the behaviour of the reserve regarding the nation’s money supply through the Central Bank. The objectives of the monetary policy are to maintain price stability and ensure an adequate flow of credit to the productive sectors of the economy. Thus, adjusting the stability of the national currency, growth in employment, and income, the monetary policy affects the real sector through long and variable periods while the financial markets are also impacted by short-term implications. Increasing uncertainty has led the Central Bank to further expand unconventional policy measures, including quantitative easing, while governments with adequate fiscal space continued to provide additional stimulus.
Restructuring the external debt is a key point for sustainable debt management of the country. Therefore, it is essential to discuss the countries with large debt such as China, India, and Japan, especially for managing debt repayment.
It is an essence of the government revenue to increase taxation with proper planning on how to allocate the tax money for government expenditure.
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) and Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) startups should be focused on advancement in technologies.
Adjusting welfare programmes and cash transfer programs effectively to the beneficiaries is essential. Annually the programmes can be cut to reduce the beneficiaries with potential employment in an informal or SME sector.
The productivity of the economy can be improved with the development of human capital in a country. Investing in the technological advancement of the education system will lead to improve human capital development.
The government and private sector need to promote establishing more industries and extra labour in the government organizations should be transferred to those agricultural,
industrial, and service industries in the country. Because unproductive labour in the government is a burden on the economy, it costs our tax collection in the budget and weight on the expenditure.
The establishment of an organization for Public-Private Partnerships for export-oriented production is a solution for the forex crisis.
Privatization and restructuring the SOEs to gain the benefits out of those industries with proper management are vital.
Opportunities behind the Crisis
When an economy is at the bottom of the economic cycle, any government thinks and leads the reforms of the economic systems in it. Therefore, new ideas for economic changes need to be promoted to improve the competitiveness of the economy and enhance productivity. The Sri Lankan tourism sector has also been affected by the economic crisis. Therefore, now the country has new opportunities to improve the quality of the services and promote the tourism industry to reach a competitive edge. SMEs are considered the backbone of the economy. The concept of competitiveness of different levels (enterprise, industry, country), has attracted policymakers. The competitiveness of small and medium-scale enterprises can be seen through the competitiveness of price, service quality, gross profit, planning, and achieving business goals compared to their competitors.