03 Feb 2017 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 Transparency in the business world—think of buyers and sellers rating each other on eBay, Airbnb and Uber—is generally considered a good thing. It accelerates information gathering, helps people coordinate their efforts and makes those in positions of authority accountable to others.
Transparency in the business world—think of buyers and sellers rating each other on eBay, Airbnb and Uber—is generally considered a good thing. It accelerates information gathering, helps people coordinate their efforts and makes those in positions of authority accountable to others.
What about transparency within organisations? Again, many emphasize the benefits of sharing information freely, as a way of empowering frontline employees and improving the quality and speed of decision-making. For example, transparency is one of the key principles in the increasingly popular Scrum methodology for project management: “In my companies, every salary, every financial, every expenditure is available to everyone,” says Jeff Sutherland, its inventor. Compared to knowledge hoarding and secretive behaviour, it is easy to agree that greater information sharing is a good thing.
But there is also a ‘dark side’ to transparency. Excessive sharing of information creates problems of information overload and can legitimize endless debate and second-guessing of senior executive decisions. High levels of visibility can reduce creativity as people fear the watchful eye of their superiors. And the open sharing of information on individual performance and pay levels, often invoked as a way of promoting trust and collective responsibility, can backfire.
There is a fascinating paradox in all this. It’s possible in a digital age to track activities in real time and to share information widely at almost zero cost (in theory, at least, improving decision-making). But, in many cases, the innovations that have brought this about have reduced effectiveness, thanks to an emerging ‘accountability gap’, where information is in the hands of people who may not use it wisely.
Executives may therefore need to become smarter about when to open up and when to withhold information. This article looks at three main areas where too much transparency creates problems and offers some guidance on how to get the balance right.
Transparency in day-to-day business activities
Thanks to technology, companies can now monitor business activities in minute detail, from verbatim logs in a call centre to real-time GPS tracking of component supplies. Such information isn’t necessarily restricted to top executives: some firms now make video recordings of their meetings so everyone can see what went on; others have opened up their strategy-making process by allowing employees across the firm to read and review a wide range of planning documents.
The argument for transparency lies in the wisdom-of-crowds effect: by broadening the number of people involved, we will make smarter decisions and we will increase buy-in. But there are also problems with this approach. One is lack of speed: “It takes us so much longer to make decisions because so many people are involved,” admits Jim Whitehurst, CEO of software company Red Hat, which has pioneered a highly inclusive approach to strategy-making.
The other, and bigger, concern is that people weigh in without relevant knowledge or without any responsibility to see things through. One university we know well provided the faculty with detailed information about the student demand for elective courses, resulting in a number of proposals to cut certain courses and grow others. The proposals were well intentioned but were later rejected because the faculty did not know the trade-offs that had to be managed to introduce new classes. Both the faculty and senior management were frustrated.
Some companies have sought to overcome this accountability gap. For example, the Amazon subsidiary Zappos recently experimented with an ambitious form of self-management called holacracy, in which work is done in self-governing teams without any formal management roles and the employees have a “duty of transparency.” But implementing this new transparent way of working has not worked for everyone, with 14 percent of workers choosing to leave since it was introduced.
One study noted that it “has been confusing and time-consuming, especially at first, sometimes requiring five extra hours of meetings a week as workers unshackled from their former bosses organise themselves into ‘circles.’” Another company, Shift (founded by former Zappos manager Zach Ware), abandoned holacracy after less than a year because it led to too many meetings and vague decision-making authority.
Such cases reveal an important truth: many people do not want to know the full details of how their firm is doing, nor do they want to be held fully responsible for its outputs. Instead, they want to know enough to do their job well and they want to have the right to know more but for the most part they are happy for someone else to process and manage that information on their behalf.
So how do you get the balance right? The first rule of thumb is to strive for a match between transparency and responsibility. If client service is everyone’s responsibility, then data on service levels should be available to all; but if decisions about which product lines to invest in and which ones to cut are the CEO’s responsibility, he or she should have privileged access to the information needed to make those decisions.
If the employees can access this type of privileged information anyway, it is useful to create a team or task force with responsibility for sifting through and channelling the views of employees to the ultimate decision makers. A works council in Germany or an employee committee like the one at retailer John Lewis can give employees a voice without the entire decision-making process grinding to a halt.
Transparency in employee efforts and rewards
Employee earnings is a second and highly controversial dimension of transparency. About one-third of US companies have ‘no disclosure’ contracts that specifically forbid employees from discussing their pay with coworkers. In most others, pay is implicitly a private matter between the boss and employee. But in recent years a number of firms have experimented with radical pay transparency, even in large firms such as Whole Foods Market. Reasons for this shift include a desire to treat employees as adults, increase trust and spur competition.
But sharing pay information can backfire—badly. Consider the example of a Canadian engineering firm. Each year, just before Christmas, the founder and CEO of the 30-year-old company used to look over each employee’s contributions for the year and then award each person a bonus based on his personal beliefs about the value of those contributions. Sometimes the bonuses would be large—say US $ 30,000—and other times the bonuses would be small (US $ 5,000 or nothing at all). There was no formula, only the judgment call of the founder.
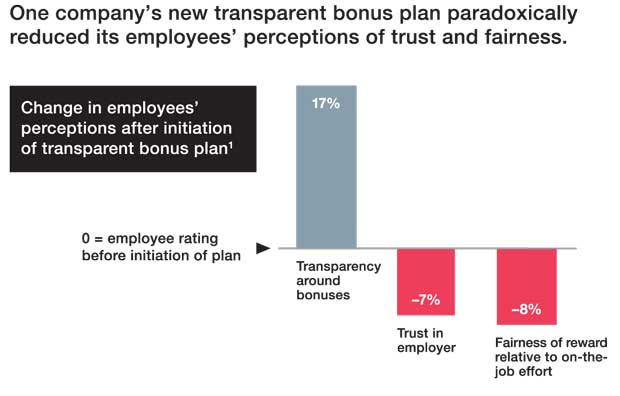
As the organisation grew, however, the CEO requested that the company leaders develop a rational and transparent process for determining the allocation of bonuses. The leaders worked for a year to create a fair bonus system based on pre-established key performance indicators and launched it through town halls and workshops so that everyone was clear how their bonus would be calculated. A year later, after the bonuses had been calculated and distributed according to the new system, the employees acknowledged the increased transparency, but their perceptions of the fairness of the bonuses were significantly worse and they trusted the employer less (exhibit). Even those who had received as much or more than the previous year were significantly less satisfied with the fairness of the more transparent system and trusted the employer less.
What went wrong? Interviews we conducted with the employees suggested two unintended side effects of the new process. First, transparency invited a critical and transactional evaluation, rather than the bonus being seen as an unexpected gift. Second, transparency highlighted those who received larger bonuses, inviting envy on the part of those who fared less well.The company leaders were genuinely surprised and have had to train the managers to have tough monthly conversations, which can be facilitated through better data and clearer expectations about performance criteria.
This case illustrates the psychological phenomenon of social comparison, whereby people have a need to compare themselves to others. In the workplace, we are driven to compare the equity of our contributions (inputs) and rewards (outcomes) relative to others. Perceiving our ratio of rewards to contributions as worse than other people’s creates mental dissonance that can spiral into envy, distraction, stealing, withdrawing effort, or quitting. Greater transparency was supposed to increase the perceptions of equity at the Canadian engineering firm, but its emphasis on outcomes (rather than inputs and outcomes) had the opposite effect. The employees focused on “gaming” the mechanics of the system rather than creating real value and thinking about the collective good. As a result, the senior executives had to put in a lot of additional work, meeting with the employees to explain more clearly how the new scheme actually worked. In hindsight, one of them noted, “It would have been useful to announce and run the new bonus system as a ‘phantom’ for the first year, telling the employees what they would have earned under the new system and then allowing them voice about the pain points of the new system.”
In sum, even though many firms are experimenting with pay transparency, we believe they should be cautious and only do it when they can clearly connect the employees’ inputs to the outcomes they achieved.
Transparency in creative work
The third area where transparency can backfire is in creative work.
In many circumstances, such as working on an oil rig where safety comes first, making actions visible to others is a good thing. But in other circumstances it can have its downsides. Creative work, in particular, with its nonlinear detours and dead ends, does not benefit from high levels of transparency. Indeed, the close monitoring of the process of developing a creative product is detrimental because the creative person may self-censor some of his or her better ideas, for fear that they will be misunderstood or criticized. For example, one study found that workers in a mobile-phone factory actually did their most productive and creative work when they were not being observed, suggesting that performance improvements can sometimes be achieved by creating “zones of privacy.”
Consider the case of Eulogy, a communications agency based in London, where CEO Adrian Brady has sought to increase transparency in his team’s creative work by bringing the clients into early-stage brainstorming sessions. While this approach has ultimately proven useful, Euology’s experience also shows it can give rise to negative side effects.
One problem is that clients can reject early-stage ideas before there is a chance to develop them fully. “A client’s immediate negative reaction to a potentially great idea can end a conversation before it takes flight, making it hard to do anything big or new,” explained Brady.
Another issue with full transparency is that clients don’t fully understand the process they are observing. “Sometimes a winning creative idea that is perfectly suited for a client’s brief is something that pops into our heads within minutes,” said Brady, whereas in other cases it can take many weeks. When clients have a “time-and-materials mind-set” they’re likely to focus on how long it took to get the idea, rather than how much value it will generate.
Eulogy’s original and highly successful campaign for the beer company Grolsch, for example, was based on a single brainstorming session. “Logically, clients know they pay us for our expertise, experience and creativity in the right idea,” Brady observed. “But emotionally, it can be hard for people to pay us if they know it took 15 minutes to generate.”
A similar sort of challenge faces companies that make video recordings of meetings and then post them online for all employees to review. One company tested this new approach for a year, but with mixed results. While seen as a big step forward in accountability, some executives were seen to talk freely in ways that reflected negatively on, and offended, employees. The executives subsequently became more cautious in their meetings, self-censoring their comments and taking all the important conversations offline.
To overcome these issues the executives should identify the truly creative activities in their firm. Which elements of work proceed on a “one step back, two steps forward” basis and which take place according to a predictable linear sequence of steps? They can then build “windows” into the process through which individuals not involved (either outsiders or interested employees from other parts of the organisation) can review progress and take stock. Typically those individuals will be happy if they know in advance where the windows are.
The stronger the level of trust between those doing the creative work and those overseeing it, the larger the windows can become.
We are getting used to transparency in our lives. We allow companies to know where we are physically and what we are thinking about and searching for. There are some 1.18 billion active users on Facebook every day, many of whom are updating their information for all to see. But transparency can also cause pain without much gain. Smart leaders need to know when to share and when to keep things back. They should also know when to get immersed in the details of a project or activity and when to turn a blind eye. Transparency is vital, but it has a dark side and it takes real skill to get the balance right.
(Julian Birkinshaw is a Professor of Strategy and Entrepreneurship at the London Business School, where Dan Cable is a Professor of Organisational Behaviour)
09 Jan 2025 3 hours ago
09 Jan 2025 4 hours ago
09 Jan 2025 7 hours ago
09 Jan 2025 7 hours ago
09 Jan 2025 8 hours ago