24 May 2016 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
An efficient and proactive stock market requires a fine blend of regulation and enforcement. The entire spectrum of enforcement transcends the scope of the regulator and stipulates appropriate investor behaviour. Accordingly, trading halts and suspensions are two enforcement initiatives that require suitable investor decision-making if the market stakeholders are to attain the ultimate goal of efficient markets.

Enforcement is the live wire of regulation
A sound and well structured regulatory system is the live wire of efficient and proactive stock markets. Achieving these two objectives do not only depend on sound regulation but also involves effective enforcement (initiatives taken to make sure that people do what is required by law). Enforcement increases credibility and enhances investor confidence in the stock market. Many are of the view that enforcement is limited to the regulator. However, the entire spectrum of enforcement goes beyond the regulator. Market participants (investors) play a predominant role in the enforcement process.
Accordingly, the article will elaborate on two key enforcement initiatives: Trading halt and suspension. The objective of the article is to disseminate the importance of the aforesaid enforcement initiatives. It will also discuss the appropriate investor psychology required for the efficient realization of these enforcement actions.
Enforcement tools: trading halt and suspension
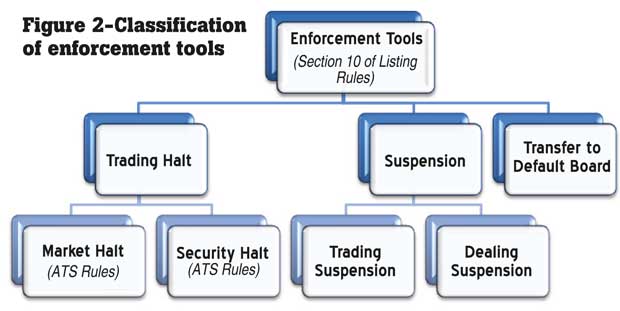
Section 10 of Listing Rules of the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) stipulates three forms of enforcement mechanisms: Transferring to the Default Board, trading halts and suspensions. Trading halts and suspensions would be the focal point of discussion in the article predominantly due to its vital role of protecting the interest of investors and maintaining efficient markets. The importance is endorsed universally and is widely employed by developed stock markets to maintain efficient markets. Our readers might recall how China halted the day’s trading within 30 minutes of opening in January 2016 as shares plunged by more than 7 percent.
Trading halts
A trading halt is typically defined as a temporary suspension in the trading of a particular security on the exchange usually in anticipation of news, announcement or irregularities in transactions. A trading halt may also be imposed for purely regulatory reasons.
Section 10 of Listing Rules and Automated Trading System (ATS) Rules define the scope of trading halts in the local legal framework. As depicted in Figure 2, ATS Rules identify two types of trading halts: market halt and security halt. Market halt considers the market operations at large while the later is centralized around a specific security (stock).
In the case of market halts, the market can be halted at the discretion of the CSE during pre-open and regular trading hours. During a market halt the venue status will be displayed as ‘HALT’. The CSE can subsequently lift the halt on the market and the market will return to its Venue state prior to imposing
the halt.
As stated above security halt refers to individual securities and is imposed due to one or more of the following situations:
Prior to an announcement of any price-sensitive information of a listed entity.
To obtain a clarification from the entity on a rumour/report regarding the entity.
When an unusual movement in price/volume of a security is noted (a circuit breaker is set for individual securities (known as trip percentages). When the price of a security exceeds the trip percentage, trading in the security is automatically halted). 
If the exchange deems it necessary for the purpose of disseminating information.
To do so upon being directed by the Securities and Exchange Commission of Sri Lanka (SEC).
A trading halt may be imposed for a time period during a market day or the halt may extend beyond one day. Trading will resume as soon as the announcement/clarification from the company is disseminated to the market or when other relevant matters are addressed.
Suspension
Suspension refers to the stoppage in the trading of a security for an extended period of time. It is a much more stringent enforcement mechanism when compared to trading halts. The SEC may at its sole discretion direct the exchange to suspend the securities of any listed entity.
Suspension may be imposed on a security in the following instances:
The entity is unable or unwilling to comply with, or violates, a Listing Rule
The exchange’s rules require the suspension
By operation of law
If a trading suspension is imposed, shares of that security cannot be traded in the market until the suspension is lifted. Differently stated, investors cannot buy or sell shares of the particular company in the market. Usually trading suspensions are imposed for a longer time frame when compared to trading halts. At this juncture it is important to draw a distinction between trading suspension and dealing suspension. Dealing suspension prohibits both market transactions as well as transactions that take place away from the market (e.g.: private transfers).
Investor perception
Trading halts and suspensions might temporarily hinder the momentum of the market and securities (price movement). Amidst such downbeat sentiments, have you evaluated the importance of these enforcement actions? The SEC/CSE adopts such enforcement actions when it is of the opinion that it is required to protect the interest of investors.
Imposing trading halts will also promote an efficient price discovery mechanism by controlling market volatility/promoting price stability. Regulators work with market professionals to ensure that prices are set and clearance and settlement take place, without disruptions. Every once in a while, markets may experience events, referred to as extreme market volatility, during which prices become erratic. Trading halts would strive to curb such disruptions.
The need of these forms of enforcement actions are strongly felt due to asymmetric information (situation in which one party in a transaction has more or superior information compared to another). It will attempt to prevent certain market participants benefiting from information others don’t have access to.
Further on, suspension may affect the price adversely, the SEC would sort to such an initiative only when it believes that the public may be making investment decisions based on lack of information or false/misleading information. A suspension may also prevent potential investors from being victimized by a fraud.
It is well established that the investor is the ultimate benefactor of these initiatives. Nevertheless, correct investor psychology and appropriate decision-making are salient features required in effective enforcement. Hence, it is timely to evaluate investor perception on the subject matter.
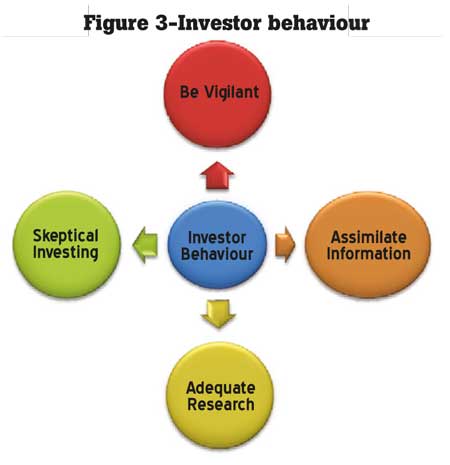
Be vigilant
If trading halts and suspensions are to be effective it is important for investors to adopt a vigilant approach. Check for reliable information and don’t be too quick to act in the market. At times it is better to miss an opportunity than regret afterwards.
Opportunity to assimilate new information
Trading halts create an opportunity for investors to digest new company information. It is imposed before companies notify the Exchange about any corporate developments that could affect trading activity in the stock. Investors should infer into the reasons for such a halt.
Perhaps the piece of information might refer to the financial health of the company (major corporate transactions like restructurings or mergers, significant positive or negative information about its products, changes in the management and legal or regulatory developments that affect the company’s ability to conduct business). It is important to make calculated decisions.
Adequate research
Always research a company before buying/selling the stock, especially following a trading halt. Consider the company’s finances, organisation and business prospects prior to engaging in transactions. You could obtain information from the CSE/SEC website, the SEC directives, etc. It is also advised to be watchful when accepting information disseminated in social media/blogs.
Be an unconvinced investor
Investors should bear in mind that these enforcement initiatives (specially trading halt) do not necessary mean that it would hold an adverse impact. At times it might be imposed prior to issuing annual reports. On the other hand, it might be to clarify certain information. Hence, what is most important is to be sceptical. Don’t make your judgments until you critically evaluate the situation.
Reverse investor psychology
Even though investors are expected to be vigilant when trading halts/suspensions are imposed, certain individuals fail to adopt such a precautionary approach. This is manifested when certain individuals attempt to promote a company (subjected to trading halt) that is faced with some regulatory issues. It could be suggested that they are reluctant to give due consideration to the observations made by the SEC. Figure 4 is an extract of a blog that promoted a stock without sufficient reasoning. The recommendations were rather abrupt.
It is of paramount importance to bear in mind that effectiveness of these enforcement actions are interlinked with investor behaviour. Thus, it is vital for investors to make calculated decisions and thereby be actively involved in the growth story of the local equity market.
10 Jan 2025 1 hours ago
10 Jan 2025 2 hours ago
10 Jan 2025 3 hours ago
10 Jan 2025 5 hours ago
10 Jan 2025 5 hours ago