17 Aug 2018 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 The liver, the largest organ within the human, performs an array of tasks that are vital for the body’s functioning. These functions include regulating the amount of sugar, protein and fat entering the bloodstream, manufacturing proteins, detoxifying blood, metabolising drugs and secreting bile to
The liver, the largest organ within the human, performs an array of tasks that are vital for the body’s functioning. These functions include regulating the amount of sugar, protein and fat entering the bloodstream, manufacturing proteins, detoxifying blood, metabolising drugs and secreting bile to
digest food.
It is normal to have a little fat in your liver But when this fat exceeds the limit and become too much, the condition is called ‘Fatty Liver’.

According to a research paper from the Harvard Medical College, fatty liver disease is becoming more common in Asia. ‘Nature’, international science journal says that “researchers have found a strong connection between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and the bacteria that inhabit the intestines.” They say the condition is starting to be seen in children probably due to their genetic susceptibility and high - fat diet. According to ‘American Liver Foundation’, patients with the most cases associated with fatty liver fall between the age group 40 - 60.
We spoke to Dr. Ranjith Abeywardene, former Ayurvedic Advisor to the Tourism Ministry and Tourism Promotion Bureau, to find out why fat deposits in the liver.
“Excess fat stored in the liver damages it. The majority of patients do not know whether they have fatty liver or not. This condition is usually detected during certain scans, done to check the possibility of other diseases or the ones done due to mere suspicion.
Liver damage starts with a swelling in the liver and fluid builds up in the abdomen. Untreated Grade 1 condition eventually becomes Grade 2
But according to Ayurveda, a doctor does a physical exam focusing the abdomen. He presses the right corner of the abdomen and checks if there is an enlargement. An obese person will have the urge to vomit and difficulties in digestion. These are the symptoms of fatty liver. An experienced Ayurvedic practitioner will soon discover a person with fatty liver when the above symptoms are visible. He will also check the pulse. They will also check the nails and eyes, to see whether they show signs of yellowing (Jaundice)” Dr. Abeywardene said.
Middle aged people are the most vulnerable to develop fatty liver. In the long run, the functioning of the liver might start to fail. The fatty liver disease is quite common among people above 40 years of age. Usually around age 35, both men and women are prone to this condition. Children are susceptible to this disease at any age. Some medicines used in treating mental and skin disorders can increase the risk for a person to develop fatty liver.
Gallbladder and pancreas are vital in the digestion of food. If this process is impaired, it can lead to other complications with regard to the processing and absorption of food. These complications lead to cancers and as a result liver transplants are neeed. But this critical stage can be easily avoided by consuming healthy and local food and also by following a healthy routine.” Dr. Abeywardene noted.
Two basic types of Fatty liver
The extra fat in the liver might distrupt its’ functioning and since the liver is purifying the blood by filtering toxins, you might become seriously ill due to disturbed filtering.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
An enlarged liver, pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen might be AFLD, which is preventable and gets better if alcohol consumption is stopped. “Regular use of alcohol exposes your liver to risk since it can trigger alcoholic hepatitis.
This will result in fever, vomiting, abdominal pain, nausea and jaundice. Scar tissue building up in the liver is called alcoholic cirrhosis. It can cause the same symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis and enlarged spleen, high blood pressure and liver failure. The worsening of liver damage can only be stopped if one quits drinking. If one has reached the maximum level of harm, a liver transplant is done. You are in danger of developing AFLD if you are obese or if you are a woman who consumes more than one drink a day” he said.
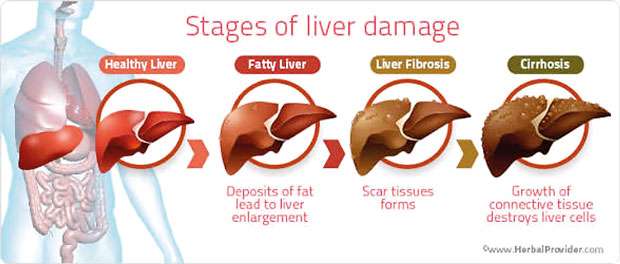
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
This is a range of liver conditions affecting people who consume a little alcohol or none at all. Too much fat storage in the liver cells, in the long run, can turn into cirrhosis or liver failure. This condition is increasing throughout the world.
The simple fatty liver is the beginning of NAFLD and it does not cause inflammation in the liver, but has the potential to become Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis with inflammation. During this stage, the above symptoms can grow into Cirrhosis (scars in the liver that don’t heal) which leads to liver failure and liver cancer. Meanwhile, some people have fatty liver Grade 1 during their entire life but are unaware of it.
Grade 1 fatty liver
“There is fat stored in the liver in small amounts. However this is not a life-threatening condition. But this is a clear warning to avoid eating oily food, sugars, salt, processed food (including sausages and meat), genetically modified food, broiler chicken (treated with hormones), all baked food (wheat flour) and sugar.
People are advised to do a lot of exercises daily and reduce weight. If not, grade 1 will become grade 2. Alcohol must be avoided if you observe signs of fatty liver. Continued alcohol consumption damages the liver” the doctor said.
Signs of Grade 1 fatty liver
Grade 2 fatty liver
Liver damage starts with a swelling in the liver and fluid builds up in the abdomen. Untreated Grade 1 condition eventually becomes Grade 2. Liver cells begin being destroyed at this level. Limiting the calorie intake and engaging in regular exercises can lower the risk of fatty liver.
An enlarged liver, pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen might be AFDL, which is preventable and gets better if alcohol consumption is stopped
Treatment
Medical treatments, exercises and a controlled diet are mandatory to survive a sick liver. There are no specific medications to this disease.
Chickpeas, green gram, green vegetables, Kola Kenda (Heen Bovitiya {octandra}, Monarakudumbiya {little ironweed}) and fish consumption can lower the risk of fatty liver. Changing the lifestyle would help in controlling or reversing fatty liver disease. Regular exercise and keeping the body weight under control helps a lot. Food should be prepared in a healthy manner with less oil, sans artificial sweeteners.
Is Arishta harmful to the liver?
Dr. Abeywardene commented on the myth that Ayurvedic syrup (Arishta) damages Liver. “It is untrue. This fake news is purposely spread to drive fear into patients make them move away from Ayurveda treatments. Taking the prescribed dose will never harm the liver. I have never seen a patient falling sick by consuming this medicine according to the doctor’s prescription. Do they know how much harmful substances are there in western medicines? How many of them have fallen sick due to the excessive use of western drugs and medicine?
“It is a sarcastic question asked by some alcohol addicts when they are prescribed medicine. Once we found a person who had consumed an Ayurvedic syrup called “Dasamularishtaya” for 30 years; consuming the syrup daily. It had damaged his liver. It is true, but he had done it according to his own will. These are stories spread by rivals to sling mud at Ayurveda. Sadly, the authorities responsible for the administration of Ayurveda don’t stand up against what’s been said.
“During modern times we have seen liver diseases becoming common. In the past, people consumed Ayurvedic medicine more often and were healthier” Dr. Abeywardene concluded.
22 Dec 2024 3 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 3 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago