05 Oct 2018 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 The human body comprises millions of cells. In a healthy person these cells grow, divide, form new cells and die in a controlled manner. However due to environmental factors, diet, genetics or simply due to random chance, this control can be lost in some of the cells. This will result in the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells which can not only outlive their ‘normal’ counterparts, but also divide much faster. When this occurs in a solid organ it will form a tumour which can be felt or if its in an internal organ detected via radiological imaging like Ultra Sound, CT or MRI scans. Hence, this condition is identified as a cancer.
The human body comprises millions of cells. In a healthy person these cells grow, divide, form new cells and die in a controlled manner. However due to environmental factors, diet, genetics or simply due to random chance, this control can be lost in some of the cells. This will result in the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells which can not only outlive their ‘normal’ counterparts, but also divide much faster. When this occurs in a solid organ it will form a tumour which can be felt or if its in an internal organ detected via radiological imaging like Ultra Sound, CT or MRI scans. Hence, this condition is identified as a cancer.
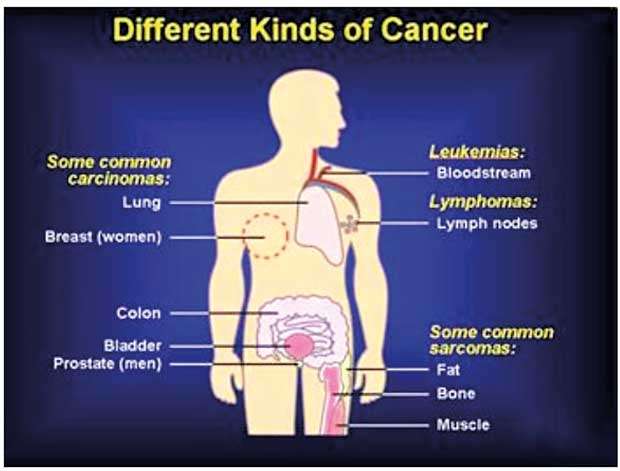
Where can you develop a cancer? – Cancers can occur in almost every part of the body. According to the cell which the cancer starts from they are divided into several types. Some of them are:
Carcinoma – Starts from cells that line the outside and the inside of the body. These are the commonest type of cancer in adults. Eg: Breast carcinoma, Lung carcinoma, Colon carcinoma etc.
Sarcoma – Arises from cells in bones and other soft tissues like muscles, fatty tissue, fibrous tissue. Eg: Osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, Leiomyosarcoma etc.
Leukaemia – A cancer originating from blood forming cells. It starts in the bone marrow and enters the blood stream. Depending on the time taken to progress it can be classified as acute or chronic. Leukaemias are further sub divided according to the type of white blood cell (Lymphocyte, Myelocyte) affected. The commonest cancer in children by far is Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia.
Lymphoma – Starts in lymph nodes or other tissues of the immune system. It is commonly present with enlarged lymph nodes. There are two main types of lymphomas. (Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma)
Brain and spinal Cord cancer– It originates from neural tissues. Exact site and type varies according to the tissue involved. These cancers do not usually spread to other parts of the body. Eg: Gliomas, Medulloblastoma, Ependymoma etc.
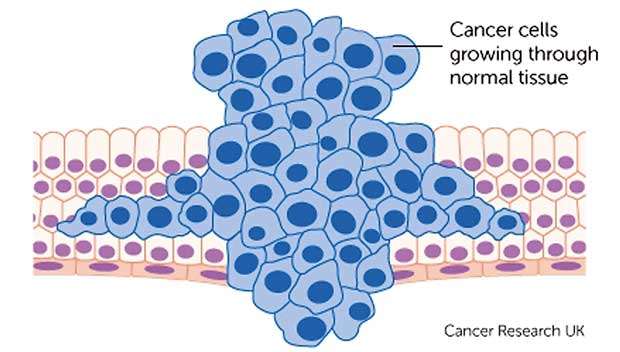
The spreading of a cancer
Differentiated cells are confined to one part of the body. Eg: Liver cells are seen only in the liver. However cancer cells have a unique ability to start from one part of the body (eg: breast) and spread to a totally different part. (Eg: Lungs, liver, bones). This spread can be through direct extension, blood stream or lymphatics. This ability makes them hard to eradicate from the body. This also means that if you detect a cancer early before it has started to spread there is a better chance of complete cure.
Common types of cancers
When you take both sexes together worldwide lung cancer is the commonest cancer followed by breast cancer and colon cancer. The situation in Sri Lanka is slightly different. The commonest cancer in Sri Lankan males is cancer of the mouth and surrounding areas followed by lung cancer. In females in Sri Lanka breast cancer has the highest incidence by far. Uterine cervix and thyroid cancers come next.
Is cancer incidence increasing?
Yes, there is a trend of increasing diagnosis of cancer patients. There are multiple causes for this. Cancers commonly occur in aged cells. With current medical advances we live longer compared to several decades ago. Therefore the chances of a cancer occurring is higher in the present day human being. There is an increasing number of cancer causing agents in the environment of today. This increased exposure to harmful environmental agents might be another reason for the increase in cancer incidence. Lifestyle changes have also contributed to rising cancer incidence. The best example of this is poor diet, substance abuse and a sedentary lifestyle. In developing countries improving medical care leading to better detection of cancers that previously when undiagnosed might be an additional contributory factor. Therefore a combination of all these factors can explain the rising incidence of cancer. An encouraging fact is that although the number of cancer patients is increasing in most countries deaths due to cancers are decreasing. This is mainly due to the successes of the modern cancer medicine.
Are all cancers fatal?
| Dear Readers, Health Capsule will be introducing a weekly series of articles on various topics related to cancer, their causes, diagnosis, treatment, etc. commencing with today’s edition. The weekly series will feature the expert opinion of Dr. Sanjeeva Gunasekera, Consultant in Paediatric Oncology, National Cancer Institute, Sri Lanka (Apeksha Hospital). Stay tuned with Health Capsule as we bring you the latest and the most informative updates on the various intricacies surrounding cancer and on how best to overcome the disease. |
No. When it comes to aggressiveness there is a lot of variability in cancers. Some cancers can be completely cured with minimum treatment while in some, even with very aggressive treatment, chances of complete cure is remote. However with the current medical advances outcomes of cancer treatments are rapidly improving. Even if complete cure is not possible novel treatment methods can help cancer patients by prolonging life, relieving symptoms and improving the overall wellbeing.
Preventing cancer
Some cancers can be prevented. Today we know that some agents will directly increase the risk of a cancer. Reducing the exposure to these agents can decrease the chance of you developing a cancer. Eg: Tobacco smoke. It is clearly proven that abstaining from smoking can greatly reduce the occurrence of some types of lung cancers.
(The writer is a Consultant in Paediatric Oncology and serves at Apeksha Hospital, formerly known as National Cancer Institute)
22 Dec 2024 3 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 3 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago
22 Dec 2024 6 hours ago