03 May 2021 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
Aflatoxin is a toxin produced by fungi and these fungi grow well under hot and humid conditions in decaying vegetables in soil
Aflatoxins were isolated and characterized in the 1960s after the spread of X Disease in turkeys. This disease killed more than 100,000 birds (Turkey) in Europe.
killed more than 100,000 birds (Turkey) in Europe.
The toxicity was discovered to be due to peanut meal produced in South America being contaminated with aflatoxins.
Turkeys are very sensitive to aflatoxins as cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism of aflatoxin B1 in the liver is efficient while glutatathion X-transferase mediated detoxification is deficient.
Aflatoxin is a mycotoxin mainly produced by two fungi Aspergillus flavurs and Aspergillus parasiticus. These fungi grow well under hot and humid conditions in decaying vegetables in soil. The fungi produce four major toxic aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 which are present in almost all major food crops.
Animal metabolism produces aflatoxin M1 and M2 from metabolism of aflatoxin B1 and B2. These compounds are found in milk including Brest milk.
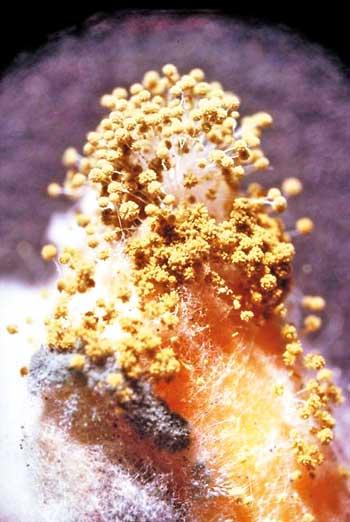 Food crops are contaminated either pre-harvest or post-harvest. In considering pre-harvest contamination, crops commonly affected are maize, cottonseed and peanuts. Post-harvest contamination occurs mainly in coffee, rice and spices. Improper storage under warm and humid conditions leads to contaminations. In coconut when improperly dried copra is stored under humid conditions the fungi grow on the copra and secrete aflatoxins.
Food crops are contaminated either pre-harvest or post-harvest. In considering pre-harvest contamination, crops commonly affected are maize, cottonseed and peanuts. Post-harvest contamination occurs mainly in coffee, rice and spices. Improper storage under warm and humid conditions leads to contaminations. In coconut when improperly dried copra is stored under humid conditions the fungi grow on the copra and secrete aflatoxins.
When coconut oil is produced from contaminated copra aflatoxins will be present in the coconut oil. Organic crops not treated with fungicides are more susceptible to contamination with aflatoxins.
Toxicity
"Aflatoxin is present in most foods. It is important to monitor the food we consume to establish that the levels of aflatoxin are in the acceptable levels of below 20mg/ Kg of food"
Aflatoxins, especially aflatoxins B1 (AFB1) is associated with toxicity and carcinogenicity in human and animal populations.
The international agency for cancer research has classified AFB1 as a group 1 carcinogenic.
The disease aflatoxicosis is coursed by the consumption of aflatoxins. Acute aflatoxicosis lead to death while chronic aflatoxicosis results in liver cancer and immune suppression.
Aflatoxins are mutagenic in bacteria and can cause birth defects. Children may become stunted although no direct evidence is available to come to a conclusion.
Consumption of food containing 1mg/Kg or higher of aflatoxins is likely to cause aflatoxicosis. Consumption over a period of 1 – 3 week of AFB1 dose of 20 – 120mg / Kg body weight per day is acutely toxic and potentially lethal.
In most animal species LD50 for aflatoxin vary from 0.3 – 18 mg/ Kg body weight.
The safe level for aflatoxin is considered to be 20 mg / Kg food and for infant food 10mg / Kg.
Production and removal of aflatoxins
The production of aflatoxins by fungi is temperature and moisture dependent. At high humanity, no AFB1 is produced below 200C and above 370C.
"Food crops are contaminated either pre-harvest or post-harvest. In considering pre-harvest contamination, crops commonly affected are maize, cottonseed and peanuts"
High production is observed at 280C. High temperature and drought conditions favour the growth of aflatoxin producing fungi in food crops. Aflatoxins are decomposed at temperatures from 237-3060C.
producing fungi in food crops. Aflatoxins are decomposed at temperatures from 237-3060C.
Therefore pasteurization does not remove aflatoxin in milk. Prof. Samarajeewa and co-workers reported that aflatoxin in coconut oil is decomposed by exposing as thin layers to solar radiation.
However, no work has been carried out to set up a large scale commercial aflatoxin removing method.
Biological methods for removal of aflatoxin
In 2009 a biological method was developed in Africa to reduced aflatoxin contamination in maize and groundnuts.
They produced aflasafe a mixture of non-aflatoxin producing strains of Aspergillus flavus isolated from soil.
Aflasafe is broadcast in the field and prevent colonization by aflatoxin producing Aspergillus strains.
It has been reported that there is a 99% reduction of aflatoxin contamination by using aflasafe in maize and groundnut fields.
Outbreaks of Aflatoxins contamination
1974 – Gujarat and Rajasthan: 106 deaths. Maize contaminate with aflatoxins
2003 – Kenya: 120 confirmed deaths. Maize contaminate with aflatoxins
2013 – Many countries of Europe reported contamination of milk with aflatoxins
2014 – Kenya: five brands of maize flour recalled due to contamination with aflatoxins
2021 – USA: contamination with pet food with aflatoxins
2021 – Sri Lanka: contamination of Coconut oil important from Malaysia with aflatoxins
Aflatoxin is present in most foods. It is important to monitor the food we consume to establish that the levels of aflatoxin are in the acceptable levels of below 20mg/ Kg of food.
The author, Deepal Mathew is an Emeritus Professor at Dept. of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, SLAAS General President – 2015
26 Nov 2024 26 Nov 2024
26 Nov 2024 26 Nov 2024
26 Nov 2024 26 Nov 2024
26 Nov 2024 26 Nov 2024
26 Nov 2024 26 Nov 2024