18 May 2021 - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 Senior Professor and Chair of Medicine Sisira Siribaddana, (MBBS MD FCCP FRCP), in an interview with Daily Mirror, elaborates on efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines to gain herd immunity. He presently serves at the Medical Faculty of Rajarata University. Also, he is a board member of the National Medicines Regulatory Authority (NMRA) and an Honorary Consultant Physician.
Senior Professor and Chair of Medicine Sisira Siribaddana, (MBBS MD FCCP FRCP), in an interview with Daily Mirror, elaborates on efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines to gain herd immunity. He presently serves at the Medical Faculty of Rajarata University. Also, he is a board member of the National Medicines Regulatory Authority (NMRA) and an Honorary Consultant Physician.
Excerpts of the interview:
 QWhat is your general assessment of the current immunisation process against COVI-19?
QWhat is your general assessment of the current immunisation process against COVI-19?
Immunization is the best response to the corona disease along with wearing a mask. Wearing a mask was not initially recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). But people had experience in wearing masks after their previous experiences with similar infections such as SARS and MERS. If there is a high risk of infection even double masking will be better.
 Vaccines , administered based on the emergency user licence by World Health Organisation-WHO - Pfizer, AstraZeneca (AZ), Moderna, Johnson and Johnson (J&J) and Sinopharm- can prevent the severity of the disease in almost all. Sri Lanka uses three vaccines available at the moment: AstraZeneca, Sinopharm and Sputnik V (not given approval by the WHO). Pfizer has been approved, but it is not available for emergency use in Sri Lanka. The National Medicines Regulatory Authority (NMRA) is reviewing the Bharath Biotec vaccine produced in India. WHO is about to grant approval to Sinovac, but for Sputnik and Bharath Biotec , approval may be delayed. All these vaccines prevent severity of the disease. Research reveals vaccines can protect you from infections up to eight months theoretically, but the real-world situation again is different. Lifelong protection is anticipated.
Vaccines , administered based on the emergency user licence by World Health Organisation-WHO - Pfizer, AstraZeneca (AZ), Moderna, Johnson and Johnson (J&J) and Sinopharm- can prevent the severity of the disease in almost all. Sri Lanka uses three vaccines available at the moment: AstraZeneca, Sinopharm and Sputnik V (not given approval by the WHO). Pfizer has been approved, but it is not available for emergency use in Sri Lanka. The National Medicines Regulatory Authority (NMRA) is reviewing the Bharath Biotec vaccine produced in India. WHO is about to grant approval to Sinovac, but for Sputnik and Bharath Biotec , approval may be delayed. All these vaccines prevent severity of the disease. Research reveals vaccines can protect you from infections up to eight months theoretically, but the real-world situation again is different. Lifelong protection is anticipated.
The vaccination will not induce sterilizing immunity. You will get infected, and can spread to others, but you will be protected from severe illness or death. Hence wear masks even if you are vaccinated
 I am yet to see a convincing academic paper about patients who died of COVID-19 after 21 days of full vaccination. However, there are worrying reports from India about death of doctors after being fully vaccinated.
I am yet to see a convincing academic paper about patients who died of COVID-19 after 21 days of full vaccination. However, there are worrying reports from India about death of doctors after being fully vaccinated.
There are about ten vaccines against COVID-19 in various stages of development in China. They include mRNA based (like Pfizer or Moderna), non-replicating adenovirus vector vaccines (like AZ, J&J and Sputnik) protein subunit vaccine (like Novavax) and one inhaled vaccine. Sinopharm-Beijing and Sinovac vaccines are being widely used in China and other countries.
China National Pharmaceutical Group Corporation or Sinopharm is a government pharmaceutical manufacturing company like State Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Cooperation of Sri Lanka. It has three vaccines in production; Sinopharm-Beijing, Sinopharm-Wuhan and another protein subunit vaccine. Sinopharm-Beijing is most widely used (in almost 60 countries). Japanese Encephalitis (a form of brain fever transmitted by mosquitoes with pigs being the intermediate host, that can kill young children and disable survivors), an illness rampant among young children in Sri Lanka in 1980 and 1990 is almost eradicated due to live attenuated vaccine (SA14-14-2) produced by a subsidiary of Sinopharm. It is the only vaccine approved (pre-qualified) by WHO against Japanese encephalitis. Sinovac is a Chinese private pharmaceutical company that produces Hepatitis A vaccine.
QThere is much criticism against Sinopharm. What is your view?
My personal belief, after studying research papers on Sinopharm-Beijing, is that it is a safe vaccine. That data was available in the academic article in Lancet Infectious Disease published by researchers that developed Sinopharm. Side effects are much less. It uses a tried and tested platform. This inactivated COVID-19 virus technology is used in two other successful vaccines -Sinovac (CoronaVac) and Bharath Biotec by India.
Some Sri Lankans experts said this vaccine was only tested on two monkeys. However, the reported issues -associated with inactivated virus vaccines (same platform used to develop Sinopharm) and seen with dengue vaccine, respiratory syncytial virus vaccine, and some animal vaccines- are not demonstrated during the development of Sinopharm-Beijing. Also, there were cases of severe lung disease when vaccinated people get infected. This is also not seen in Sinopharm-Beijing and all other inactivated whole virion technology based vaccines used today (Bharath-Biotec and Sinovac).
QThere is a problem in getting sufficient stocks of AstraZeneca vaccines due to constraints in supply chains. Sri Lanka needs around 600,000 doses for the second shots. Is there any option for administering the second dose with a different vaccine?
Early results of heterologous prime (first dose) boost (second dose) as AstraZeneca first dose and Pfizer second dose are available in Lancet and it shows an increase in side effects, but mainly ameliorated by paracetamol. Hence these side effects are not serious. Theoretically mixing of vaccines can boost the immune response. Many countries in Europe are now using the mix and match strategy in view of people who were given AstraZeneca vaccine doses first.
I am yet to see a convincing academic paper about patients who died of COVID-19 after 21 days of full vaccination. However, there are worrying reports from India about death of doctors after being fully vaccinated
Q There were four deaths after vaccination with AstraZeneca. What went wrong?
There is evidence of an increased risk of clotting on the veins. All disorders are preceded by low platelet count and it is due to immune mechanism. Now, there is a firm scientific basis for side effects or clotting disorders after the AstraZeneca vaccine; specially among young females after the first dose. Still these are extremely safe vaccines and the risk of Corona virus induced illness and blood clotting is far greater. Almost all who has taken the second dose of AZ vaccine say the side effects are much less after the second dose.
QAre all adenovirus-based vaccines (AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, Cansino and J&J) similar?
All are made from replication deficient adenoviruses or deleting a piece of gene from the adenovirus, so they cannot replicate. Then they insert a corona virus gene piece that produces spike protein into this adenovirus. Some genes are not altered (AZ) and others are altered for stability. Spike protein is the one that binds to the human cell and causes infection. AstraZeneca used chimpanzee adenovirus and others use human adenovirus. Sputnik V has two adenoviruses, different from each other in the first and second dose. J&J is given as a single dose vaccine. Blood clotting is reported in AZ and J&J vaccine, but not in Sputnik V. They say it is because the purification process of Sputnik V vaccine is better. Sputnik light is a single dose vaccine and it is the first component of Sputnik vaccine. It uses adenovirus 26 and is the same adenovirus used in J&J vaccine. So not all vaccines are same, but theoretically they can be mixed.
Q There are different public perceptions about vaccination. Some people believe they won’t get infected at all after vaccination. There are others believing that they will get infected, but severity of the disease will be far less. As a medical expert, how do you explain that?
The vaccination will not induce sterilizing immunity. You will get infected, and can spread to others, but you will be protected from severe illness or death. Hence wear masks even if you are vaccinated. The United States CDC recommendation is incorrect in this issue.
QHow do you look at the effectiveness of these vaccines against different types or mutations of the virus (South African, Brazilian and Indian etc) of COVID-19 virus?
The real-world evidence is that vaccines are effective against all the variants. The serious variants are termed VOC or Variants of Concern by the WHO. If the variants are spreading rapidly the timing between prime (first dose) and booster (second dose) is changed in some countries, but evidence again is lacking.
Sinopharm, Sinovac and the Indian Bharat Biotech vaccines incorporates an inactivated cold virus in “whole virion” technology, this method may provoke a broader immune response that could protect against multiple variants. mRNA (Pfizer, Moderna) and adenovirus-based vaccines (AZ, Sputnik, J&J) vaccines have focused on the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which can contain components specific to particular variants. However, in the real world, all vaccines are effective against variants.
QWhat about the time interval between the first and the second dose?
Theoretically, delayed booster dose (second dose) may produce more immunogenicity. There is evidence from the AstraZeneca vaccine about it. Giving the first dose to a large number of people may be advantageous to prevent death and severe illness rather than giving two doses to a limited number.
QWhat happened in Seychelles?
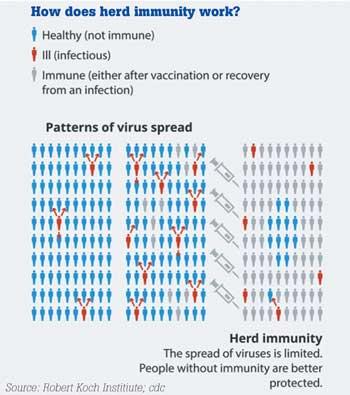
Seychelles is a small Indian ocean archipelago situated between islands of Madagascar and Maldives with tourism as the major income and with a small population (about 100,000). Till March 2021 they had 3800 cases of COVID-19 with 16 deaths. They vaccinated 60 percent of their population with two doses; 56 percent with Sinopharm and rest with AstraZeneca. In Seychells, sinopharm was given to the people people of age category between 30 and 59 years and AstraZeneca to those over 60. They developed a false sense of security and opened the borders for tourist believing they had “herd immunity” (herd immunity in vaccination is when large number of individuals in the community is vaccinated the spread of the disease from one individual to another stops-see the picture below). Since then the total cases have increased to 9184 with 32 deaths. Around 20% admitted to the hospital with COVID-19 illness has been vaccinated with two doses but reassuringly no one died. Hence all who died and other severely ill patients were not vaccinated.
25 Dec 2024 20 minute ago
24 Dec 2024 9 hours ago
24 Dec 2024 24 Dec 2024
24 Dec 2024 24 Dec 2024
24 Dec 2024 24 Dec 2024